Quantitative Phytochemical Analysis of Hevea brasiliensis and Chromolaena odorata Leaf Extracts and Yield Assessment of Their Magnesium Oxide NanoparticlesSynthesized Derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71148/tjoc/v1i1.2Keywords:
Yield Evaluation, Rubber leaf, Awolowo Leaves, Green SynthesisAbstract
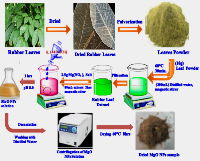
This study evaluated the quantitative yield and sustainability of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous extracts of Rubber leaf (Hevea brasiliensis) and Awolowo leaf (Chromolaena odorata) alongside magnesium nitrate hexahydrate under mild reaction conditions. The MgO nanoparticle yields were quantified and compared between the two plant sources. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis identified significant functional groups in both MgO nanoparticle samples, confirming successful synthesis. The actual yields of MgO nanoparticles were 1.39 g and 1.41 g for Rubber and Awolowo leaf extracts, respectively, corresponding to percentage yields of 58.89% and 59.74%. Quantitative phytochemical analysis revealed that Awolowo leaf extract exhibited significantly higher levels of saponins (15.010 mg/g), flavonoids (9.626 mg/g), tannins (5.145 mg/g), and alkaloids (3.351%) compared to Rubber leaf extract. These findings suggest that the phytochemical content of the plant extracts influences the synthesis efficiency and yield of MgO nanoparticles. This work highlights the potential of plant-mediated green synthesis as a sustainable approach for producing MgO nanoparticles while demonstrating the influence of phytochemical composition on synthesis outcomes.
Downloads
References
Lalithamba, H. S., Omkaresh, B. R., Siddekha, A., & Anasuya, K. V. (2023). A facile plant-mediated green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by combustion method using Terminalia chebula seed and their applications in the synthesis of selenoesters and biodiesel from used cooking oil. Scientia Iranica. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2023.62352.7792
Jeevanandam, J., Chan, Y., & Danquah, M. (2017). Biosynthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles from plant extracts via induced molecular nucleation. New Journal of Chemistry, 41(7), 2800–2814. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ03176E
Suresh, J., Pradheesh, G., Alexramani, V., Sundrarajan, M., & Hong, S. (2018). Green synthesis and characterization of hexagonal-shaped MgO nanoparticles using insulin plant (Costus pictus D. Don) leaf extract and its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activity. Advanced Powder Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APT.2018.04.003
Lalithamba, H. S., Omkaresh, B. R., Siddekha, A., & Anasuya, K. V. (2023). A facile plant-mediated green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by combustion method using Terminalia chebula seed and their applications in the synthesis of selenoesters and biodiesel from used cooking oil. Scientia Iranica. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2023.62352.7792
Lalithamba, H. S., Omkaresh, B. R., Siddekha, A., & Anasuya, K. V. (2023). A facile plant-mediated green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by combustion method using Terminalia chebula seed and their applications in the synthesis of selenoesters and biodiesel from used cooking oil. Science International. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2023.62352.7792
Singh, H., Desimone, M., Pandya, S., Jasani, S., George, N., Adnan, M., Aldarhami, A., Bazaid, A., & Alderhami, S. (2023). Revisiting the green synthesis of nanoparticles: Uncovering influences of plant extracts as reducing agents for enhanced synthesis efficiency and its biomedical applications. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 18, 4727–4750. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S419369
Mittal, A., Chisti, Y., & Banerjee, U. (2013). Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnology Advances, 31(2), 346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.01.003
Jadoun, S., Arif, R., Jangid, N., & Meena, R. (2020). Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19, 355–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01074-x
Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K., Tomaszewska, E., Małek, K., Celichowski, G., Orlowski, P., Krzyżowska, M., & Grobelny, J. (2019). The synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles with plant extracts. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 177, 19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.037
Soni, V., Raizada, P., Singh, P., Cuong, H. S., Saini, A., Saini, R., Van Le, Q., Nadda, A., Le, T. T., & Nguyen, V. H. (2021). Sustainable and green trends in using plant extracts for the synthesis of biogenic metal nanoparticles toward environmental and pharmaceutical advances: A review. Environmental Research, 111622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111622
Jadoun, S., Arif, R., Jangid, N., & Meena, R. (2020). Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19, 355–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01074-x
Khan, F., Shariq, M., Asif, M., Siddiqui, M., Malan, P., & Ahmad, F. (2022). Green nanotechnology: Plant-mediated nanoparticle synthesis and application. Nanomaterials, 12(4), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040673
Hamdy, N., Boseila, A., Ramadan, A., & Basalious, E. (2022). Iron oxide nanoparticles-plant insignia synthesis with favorable biomedical activities and less toxicity, in the "Era of the-Green": A systematic review. Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040844
Paiva-Santos, A., Herdade, A., Guerra, C., Peixoto, D., Pereira-Silva, M., Zeinali, M., Mascarenhas-Melo, F., Paranhos, A., & Veiga, F. (2021). Plant-mediated green synthesis of metal-based nanoparticles for dermopharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 603, 120311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120311
Singh, H., Desimone, M., Pandya, S., Jasani, S., George, N., Adnan, M., Aldarhami, A., Bazaid, A., & Alderhami, S. (2023). Revisiting the green synthesis of nanoparticles: Uncovering influences of plant extracts as reducing agents for enhanced synthesis efficiency and its biomedical applications. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 18, 4727–4750. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S419369
Vanlalveni, C., Lallianrawna, S., Biswas, A., Selvaraj, M., Changmai, B., & Rokhum, S. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: A review of recent literature. RSC Advances, 11(6), 2804–2837. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra09941d
Azad, A., Zafar, H., Raza, F., & Sulaiman, M. (2023). Factors influencing the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts: A comprehensive review. Pharmaceutical Fronts, 5, e117–e131. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1774289
Jeevanandam, J., Chan, Y., & Danquah, M. (2017). Biosynthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles from plant extracts via induced molecular nucleation. New Journal of Chemistry, 41(7), 2800–2814. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ03176E
Kesic, A., Marković, K., Grujović, M., & Marković, Z. (2023). An investigation of the optimal conditions for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using an aqueous extract from the Agrimonia eupatoria L. plant. IOCN 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/iocn2023-14477
Essien, E., Atasie, V., Oyebanji, T., & Nwude, D. (2020). Biomimetic synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Chromolaena odorata (L.) leaf extract. Chemical Papers, 74(7), 2101–2109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01056-x
Khan, F., Shariq, M., Asif, M., Siddiqui, M., Malan, P., & Ahmad, F. (2022). Green nanotechnology: Plant-mediated nanoparticle synthesis and application. Nanomaterials, 12(4), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040673
Karthik, K., Raghu, A., Reddy, K., Ravishankar, R., Sangeeta, M., Shetti, N., & Reddy, C. (2021). Green synthesis of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles and its application for the photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic pollutants. Chemosphere, 287, Part 2, 132081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132081
Zhang, D., Gu, Y., Huang, H., & Zhang, G. (2020). Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their potential applications to treat cancer. Frontiers in Chemistry, 8, 799. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00799
Ikhuoria, E. U., Uwidia, I. E., Otabor, G. O., & Ifijen, I. H. (2024). Comparative analysis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles biosynthesized from rubber seed shell and rubber leaf extracts. Biomedical Materials & Devices, 2(1), 1078–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-023-00139-z
Zare, M., Namratha, K., Thakur, M., & Byrappa, K. (2019). Biocompatibility assessment and photocatalytic activity of bio-hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Thymus vulgaris leaf extract. Materials Research Bulletin, 112, 110190. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATERRESBULL.2018.09
Hamdy, N., Boseila, A., Ramadan, A., & Basalious, E. (2022). Iron oxide nanoparticles-plant insignia synthesis with favorable biomedical activities and less toxicity, in the "Era of the-Green": A systematic review. Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040844
Jain, S., & Mehata, M. (2017). Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Scientific Reports, 7, 15724. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15724-8
Moreno-Vargas, J., Echeverry-Cardona, L., Moreno-Montoya, L., & Restrepo‐Parra, E. (2023). Evaluation of antifungal activity of Ag nanoparticles synthetized by green chemistry against Fusarium solani and Rhizopus stolonifera. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030548
Wang, L., Lu, F., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., & Wu, Z. (2018). Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles fast synthesized by flavonoids fraction of Psidium guajava L. leaves. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 262, 515–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2018.04.151
Otabor, G. O., Ifijen, I. H., Mohammed, F. U., Aigbodion, A. I., & Ikhuoria, E. U. (2019). Alkyd resin from rubber seed oil/linseed oil blend: A comparative study of the physicochemical properties. Heliyon, 5(5), e01621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01621
Singh, A., Joshi, N., & Ramola, M. (2019). Magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgONPs): Green synthesis, characterizations, and antimicrobial activity. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 12(10), 4727–4731. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360x.2019.00799.6
Essien, E., Atasie, V., Oyebanji, T., & Nwude, D. (2020). Biomimetic synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Chromolaena odorata (L.) leaf extract. Chemical Papers, 74(7), 2101–2109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01056-x
Singh, A., Joshi, N., & Ramola, M. (2019). Magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgONPs): Green synthesis, characterizations, and antimicrobial activity. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 12(10), 4727–4731. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360x.2019.00799.6
Zhang, M. (2024). Product yield increasing more than 20 times achieved by reducing water poisoning for direct diethyl carbonate synthesis. Langmuir: The ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c03547
Sheldon, R. (2012). Fundamentals of green chemistry: Efficiency in reaction design. Chemical Society Reviews, 41(4), 1437–1451. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15219j
Naveenkumar, R., & Baskar, G. (2020). Process optimization, green chemistry balance, and technoeconomic analysis of biodiesel production from castor oil using heterogeneous nanocatalyst. Bioresource Technology, 320, Part A, 124347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124347
Cicco, L., Perna, F., Capriati, V., & Vitale, P. (2024). A sustainable synthetic approach to tacrine and cholinesterase inhibitors in deep eutectic solvents under aerobic conditions. Molecules, 29(6), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061399
Khan, R., Adole, V., Pawar, T., & Jagdale, B. (2024). Green chemistry approach to the synthesis of 2-aryl/heteroaryl substituted 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-ones using lemon juice under concentrated solar radiations as a renewable source. RSC Advances, 14(50), 32350–32357. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra05772d
Kumar, P., Bhatlu, M., Sukanya, K., Karthikeyan, S., & Jayan, N. (2020). Synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticle by eco-friendly method (green synthesis) – A review. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.726
Lalithamba, H. S., Omkaresh, B. R., Siddekha, A., & Anasuya, K. V. (2023). A facile plant-mediated green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by combustion method using Terminalia chebula seed and their applications in the synthesis of selenoesters and biodiesel from used cooking oil. Scientia Iranica. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2023.62352.7792
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tropical Journal of Chemistry

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.